What is the purpose of annealing in the casting process?
2025-08-12 09:07:49 hits:0
Structured Outline
Definition and Basic Principles
Types of Casting Annealing
Applications of Casting Annealing
Advantages of Casting Annealing
Limitations and Challenges
Development Trends
Conclusion
Casting Annealing Process: Everything You Need to Know
In the dynamic world of modern manufacturing, the casting annealing process stands as a fundamental and indispensable technique. It is a process that not only shapes the physical and mechanical properties of castings but also plays a crucial role in determining the quality and performance of end - products across various industries.
Definition and Basic Principles
Casting annealing is a heat - treatment process that involves heating a casting to a specific temperature, holding it at that temperature for a defined period, and then cooling it at a controlled rate. This process is based on the principle that heat can alter the microstructure of the casting material. By carefully controlling the heating, holding, and cooling stages, manufacturers can achieve desired changes in the material's grain size, phase composition, and internal stress distribution, which in turn affect the casting's hardness, ductility, toughness, and other mechanical properties.
Types of Casting Annealing
Full Annealing: Full annealing is a comprehensive heat - treatment process. The casting is heated above its upper critical temperature until it completely transforms into austenite. Then, it is slowly cooled in the furnace. This slow cooling rate allows for the formation of a fine - grained, uniform microstructure. The benefits of full annealing include improved ductility and toughness, making it suitable for castings that need to undergo significant deformation during further processing. In the automotive industry, full - annealed castings are used in components such as engine blocks and transmission housings, where high strength and good formability are required.
Spheroidizing Annealing: This type of annealing is mainly used for high - carbon steels. The casting is heated to a temperature just below the critical point and held for an extended period. During this time, the carbides in the steel transform into a spherical shape. Spheroidizing annealing improves the machinability of the casting, as the spherical carbides reduce the cutting forces and wear on cutting tools. It is commonly applied in the production of tools and dies, where ease of machining is essential.
Stress - Relief Annealing: Stress - relief annealing is designed to reduce the internal stress in castings that has been generated during the casting process, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The casting is heated to a relatively low temperature (below the critical point) and held for a sufficient time to allow the stress to relax. Then, it is slowly cooled. This process is crucial in preventing distortion and cracking in the casting, especially in large - scale and complex - shaped castings used in heavy machinery.
Applications of Casting Annealing
Automotive Industry: In the automotive sector, casting annealing is widely used to improve the performance of various components. For example, annealed castings in engine parts can withstand high - temperature and high - pressure environments, while those in suspension systems offer better fatigue resistance. This leads to increased reliability and longevity of vehicles.
Aerospace Industry: The aerospace industry has extremely high requirements for the quality and performance of materials. Casting annealing helps to meet these demands by providing castings with excellent strength - to - weight ratios, high fatigue resistance, and dimensional stability. Components such as turbine blades and structural frames are often annealed to ensure their safety and functionality in extreme conditions.
General Machinery Manufacturing: In general machinery, annealing is used to enhance the machinability and mechanical properties of castings. This results in more precise and durable machine parts, which can improve the overall efficiency and performance of the machinery.
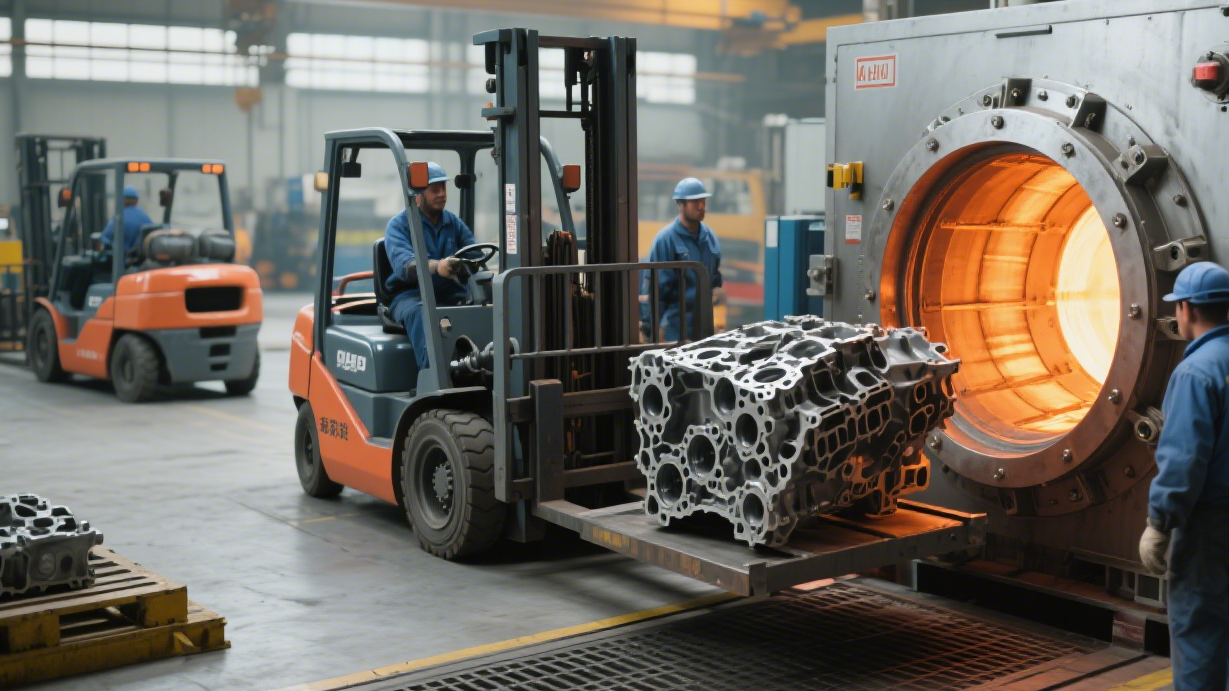

Advantages of Casting Annealing
One of the primary advantages of casting annealing is the improvement of mechanical properties. By refining the grain structure, the casting becomes stronger, more ductile, and more resistant to fatigue. Annealing also reduces internal stress, which is essential for preventing cracking and distortion during machining and service. Additionally, it enhances the machinability of the casting, reducing production costs and improving the surface finish of the final product.
Limitations and Challenges
However, the casting annealing process is not without its limitations. One of the major challenges is the high energy consumption associated with heating and cooling the castings. Moreover, precise process control is required to ensure consistent results. Improper control of temperature, time, or cooling rate can lead to over - annealing or under - annealing, which can negatively affect the quality of the casting.
Development Trends
The future of the casting annealing process is promising, with several exciting trends on the horizon. Advancements in annealing technology, such as the use of advanced heating and cooling systems, are making the process more efficient and precise. The integration of Industry 4.0 concepts, such as real - time monitoring and control using sensors and data analytics, is also improving the quality and consistency of annealing. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on sustainability, with manufacturers exploring ways to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact in the annealing process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the casting annealing process is a vital part of modern manufacturing. Its ability to improve the mechanical properties, reduce internal stress, and enhance machinability of castings makes it indispensable in various industries. Despite the challenges it faces, the continuous development of technology and the focus on sustainability are expected to drive the casting annealing process forward, ensuring its continued relevance and importance in the manufacturing landscape.
Blog Author Profile
DAWN | Pig Iron & Castings Procurement Advisor 18 years in the foundry trenches give me an edge: I know how pig iron’s chemistry impacts casting quality and can troubleshoot defects like cracks and porosity. With a 1M MT/year pig iron and 60k MT/year casting output from our in-house factory, plus 200+ verified suppliers on our platform, we offer fast price comparisons. Expect a 24-hour inquiry response—my goal? Not just closing deals, but being your go-to partner in the foundry world.
18 years in the foundry trenches give me an edge: I know how pig iron’s chemistry impacts casting quality and can troubleshoot defects like cracks and porosity. With a 1M MT/year pig iron and 60k MT/year casting output from our in-house factory, plus 200+ verified suppliers on our platform, we offer fast price comparisons. Expect a 24-hour inquiry response—my goal? Not just closing deals, but being your go-to partner in the foundry world.

 en
en  fra
fra  de
de  ru
ru  ara
ara  gle
gle  it
it  jp
jp  kor
kor  th
th  zh
zh 


