How to make pig iron?
2025-02-05 09:46:24 hits:0
The Manufacturing Process of Pig Iron: From Iron Ore to Blast Furnace Smelting

Introduction: Pig Iron – The Foundation of Steel Production
Pig iron is the foundational raw material of the steel industry, produced by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. It contains a high carbon content and is the starting point for many iron and steel products. The manufacturing process of pig iron involves complex chemical and physical reactions. Below are the key steps and principles of pig iron production.
Raw Material Preparation
The production of pig iron requires several key raw materials:
Iron Ore: Primarily composed of iron oxides such as hematite (Fe₂O₃) and magnetite (Fe₃O₄)
Coke: Acts as both a fuel and a reducing agent, providing heat and removing oxygen from the iron ore
Limestone: Serves as a flux, helping to remove impurities like silica and form slag
Air: Heated in a hot blast stove and blown into the blast furnace to support coke combustion
These raw materials are preprocessed by crushing, screening, and sintering to ensure they are suitable for blast furnace operations.
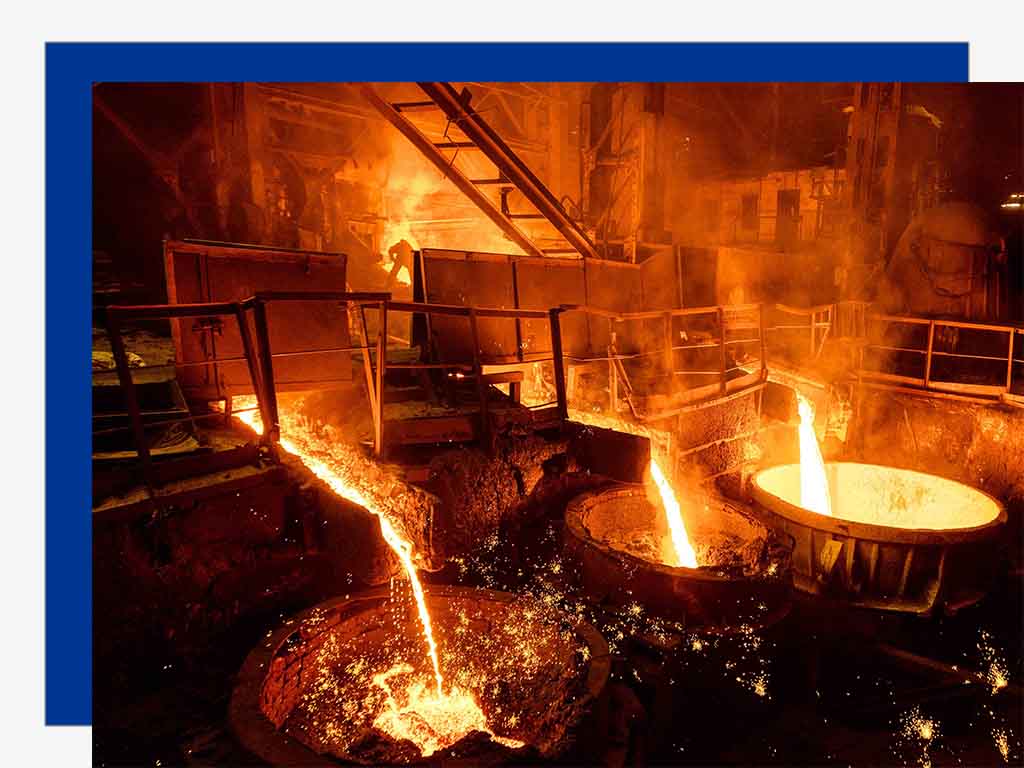

Blast Furnace Smelting
The blast furnace is the core equipment for pig iron production. It is a tall vertical furnace with temperatures exceeding 2000°C. The main stages are:
1. Charging: Iron ore, coke, and limestone are loaded into the top of the blast furnace in layers. The coke burns at the bottom, producing high temperatures and reducing gases.
2. Reduction Reactions: Iron oxides are reduced by coke and carbon monoxide (CO).
Coke combustion: C + O₂ → CO₂ → 2CO
Reduction: Fe₂O₃ + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO₂
3. Melting and Separation: Reduced iron melts to form liquid pig iron. Limestone reacts with impurities to form slag, which floats for easy separation.
4. Tapping Iron and Slag: Tap holes at the bottom allow pig iron and slag to be drained. Pig iron is sent to steel mills or foundries; slag can be used in construction.
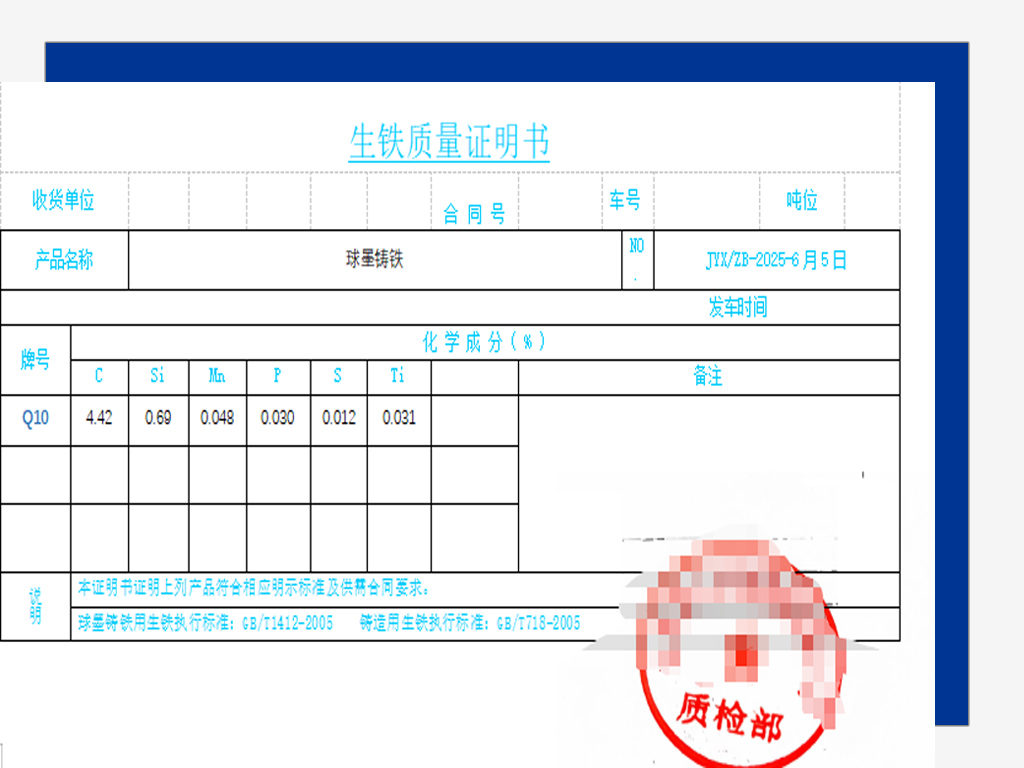
Composition and Properties of Pig Iron
Pig iron primarily consists of iron (92%-95%) with high carbon (3.5%-4.5%) and smaller amounts of silicon, manganese, phosphorus, and sulfur. Characteristics include:
High hardness but brittle
Relatively low melting point (~1150–1200°C), suitable for casting
Not directly usable for structural materials; requires further refining
| Element | Typical Content (%) | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Fe | 92–95 | Base metal |
| C | 3.5–4.5 | Hardness, brittleness |
| Si | 0.5–3 | Improves fluidity |
| Mn | 0.5–6 | Strength adjustment |
| P | 0.1–2 | Impurity; reduces ductility |
| S | 0.01–0.05 | Impurity; affects corrosion resistance |
Applications of Pig Iron
Pig iron is mainly used in the following areas:
Raw Material for Steelmaking: Pig iron is a primary raw material for steel production. Through processes like the basic oxygen furnace or electric arc furnace, its carbon content is reduced, and its composition is adjusted to produce various types of steel.
Casting: Pig iron is directly used to cast iron products, such as engine blocks, pipes, and machine tool bases.
Alloy Production: Pig iron serves as a base material for iron-based alloys, used in manufacturing wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant specialty materials.
Other Industries: Automotive parts, precision equipment, wind power equipment, aerospace components
Environmental Considerations
Traditional blast furnace smelting consumes significant energy and emits carbon dioxide, impacting the environment. In recent years, the steel industry has been exploring more environmentally friendly smelting technologies, such as:
Direct Reduced Iron (DRI): Using natural gas or hydrogen instead of coke to reduce carbon emissions.
Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF): Utilizing scrap steel as raw material to reduce reliance on pig iron.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): Reducing carbon emissions from blast furnace operations.
Conclusion
The production of pig iron is the foundation of the steel industry, and the blast furnace smelting process demonstrates humanity's ability to utilize and transform natural resources. With technological advancements, pig iron production is moving toward greater efficiency and environmental sustainability, providing critical support for the sustainable development of modern industry.

About Tiegu
Tiegau is a professional supplier of pig iron, offering a comprehensive range of products to meet diverse industrial needs. Their product portfolio includes:
Foundry Pig Iron: Ideal for casting applications.
Ductile Iron Pig Iron: Used in the production of ductile iron.
High-Purity Pig Iron: Suitable for specialized applications requiring low impurity levels.
Steelmaking Pig Iron: Designed for use in steel production.
Blast Furnace Pig Iron: A versatile product for various industrial uses.
Advantages:
Stable chemical composition
Reliable supply and competitive pricing
Extensive export experience
Contact us today for specifications or quotes.
FAQ
Q1: What is the difference between grey and white pig iron?
A1: Grey pig iron contains free carbon in the form of graphite, giving it a grey fracture surface and good machinability. White pig iron has combined carbon (cementite), resulting in a hard, brittle material that is more difficult to machine.
Q2: Why is limestone used in pig iron production?
A2: Limestone acts as a flux in the blast furnace. It combines with impurities like silica to form slag, which floats on the molten iron and can be easily removed, improving the purity of pig iron.
Q3: How is pig iron safely transported?
A3: Molten pig iron is usually cast into ingots or pigs and cooled before transportation. These solid pig iron blocks are easier and safer to handle, store, and ship to steel mills or foundries.
Q4: Which industries use pig iron the most?
A4: Pig iron is mainly used in steelmaking and casting. It is widely applied in automotive parts, precision machinery, wind power equipment, aerospace components, pipes, engine blocks, and other iron products.

 en
en  fra
fra  de
de  ru
ru  ara
ara  gle
gle  it
it  jp
jp  kor
kor  th
th  zh
zh 


